- EUR/USD trimmed near-term gains on Monday, holding above 1.0800 but declining.
- French elections delivered a less-than-solid outcome, coalition minority set for deadlock.
- US Fed Chair Powell due to testify before US federal committees this week.
EUR/USD stumbled on Monday after a muddled election outcome in France leaves policy guidance unclear for the Euro bloc. A coalition minority government win in France kept a financially-disastrous far right party out of the leadership race after a strong upset in earlier European Parliamentary elections. Still, the win was anything but decisive as a hodge-podge of coalition parties with conflicting ideologies is set for policy deadlock in France in the coming months.
Forex Today: All eyes on Powell
Federal Reserve (Fed) Chairman Jerome Powell is set to make the first of two appearances this week as the Fed head delivers the semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the US Senate Banking Committee. This will be followed up by a second appearance on Wednesday to deliver the same report to the US Congressional House Committee on Financial Services.
Later this week, key US inflation data will be released. The US Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation is due on Thursday, and the Producer Price Index (PPI) wholesale inflation is slated for Friday. Some traders who are hoping for a decrease in inflation to push the Fed into making rate cuts sooner rather than later may be disappointed. Forecasts suggest that both CPI and PPI inflation figures are expected to either remain steady or increase slightly.
Final German inflation figures will be published during the Thursday European market session. German Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HCOB) inflation is broadly expected to hold steady 2.5% YoY as inflation pressures continues to vex the Bundestag’s 2% inflation target.
Economic Indicator
Consumer Price Index ex Food & Energy (MoM)
Inflationary or deflationary tendencies are measured by periodically summing the prices of a basket of representative goods and services and presenting the data as the Consumer Price Index (CPI). CPI data is compiled on a monthly basis and released by the US Department of Labor Statistics. The MoM print compares the prices of goods in the reference month to the previous month.The CPI Ex Food & Energy excludes the so-called more volatile food and energy components to give a more accurate measurement of price pressures. Generally speaking, a high reading is seen as bullish for the US Dollar (USD), while a low reading is seen as bearish.
EUR/USD technical levels
Fiber is struggling after repeated near-term failures to breach above 1.0840, and bulls are running out of gas as the 200-hour Exponential Moving Average (EMA) rises into 1.0780, keeping a tight floor under intraday price action.
Daily candles continue to churn in the midrange of a rough descending channel through 2024, and EUR/USD is set to face a drooping technical ceiling as the upper bound eases to 1.0850.
EUR/USD hourly chart
EUR/USD daily chart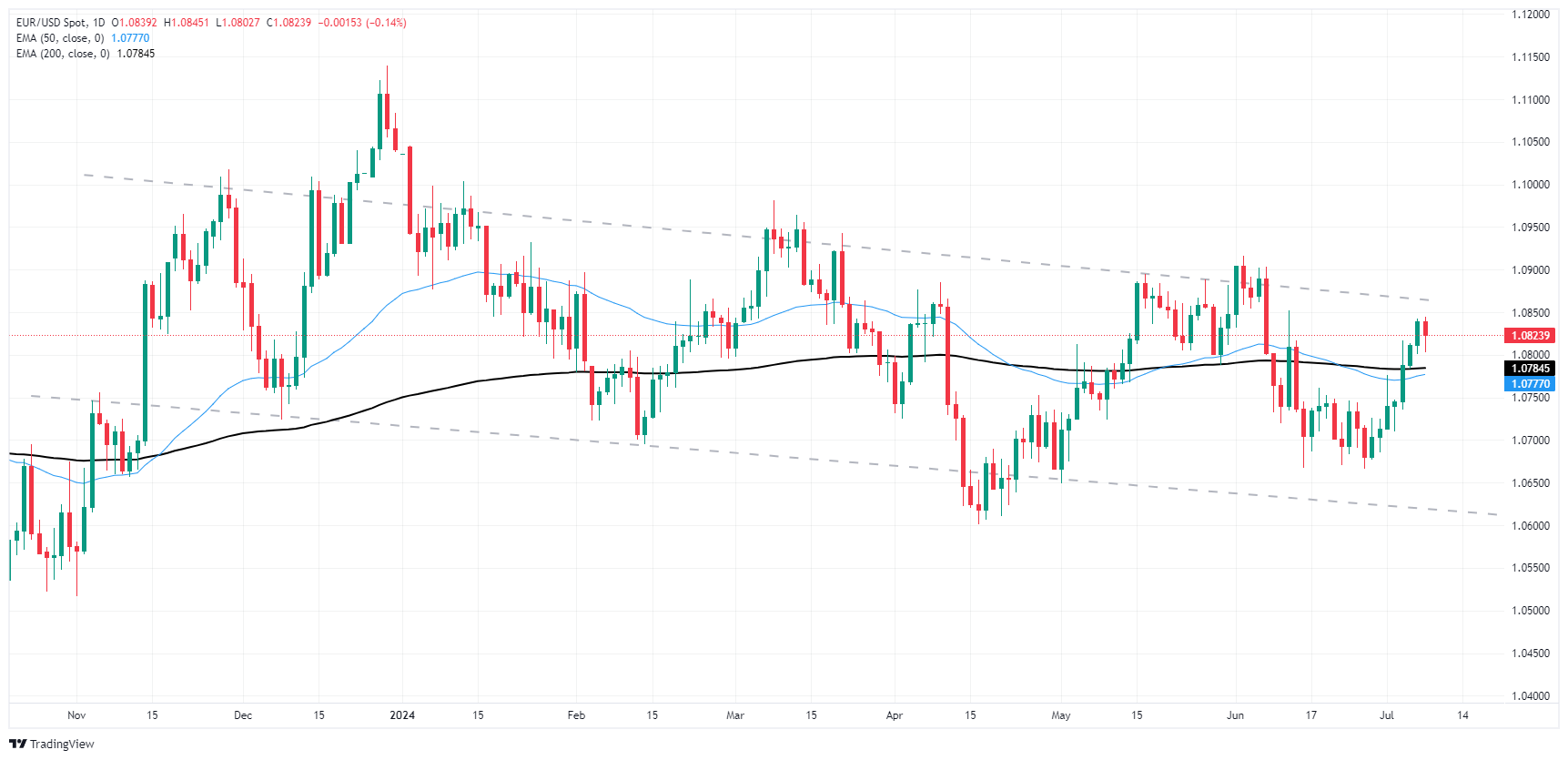
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 20 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

















